Kens Metal Industries is a leader in the distribution and transformation of special steels for the East African market.
Our company offers customers a wide range of special steels, bronze, brass, copper, nylon, cast iron and aluminium. We also provide specialized services upon customer request.
Kens Metal Industries Limited was started as a foundry in 1982 which produced, stocked and supplied Cast Iron, Brass, Bronze and Aluminium. We were initially a sand casting foundry and a machine workshop. In 1984 we started pressure die casting of brass and Aluminium, as well as that a small Brass extrusion press was installed.
Read More
Kens Metal Industries Ltd is a able to meet the needs of various market sectors, such as mining, general engineering, road, agriculture, energy firms etc
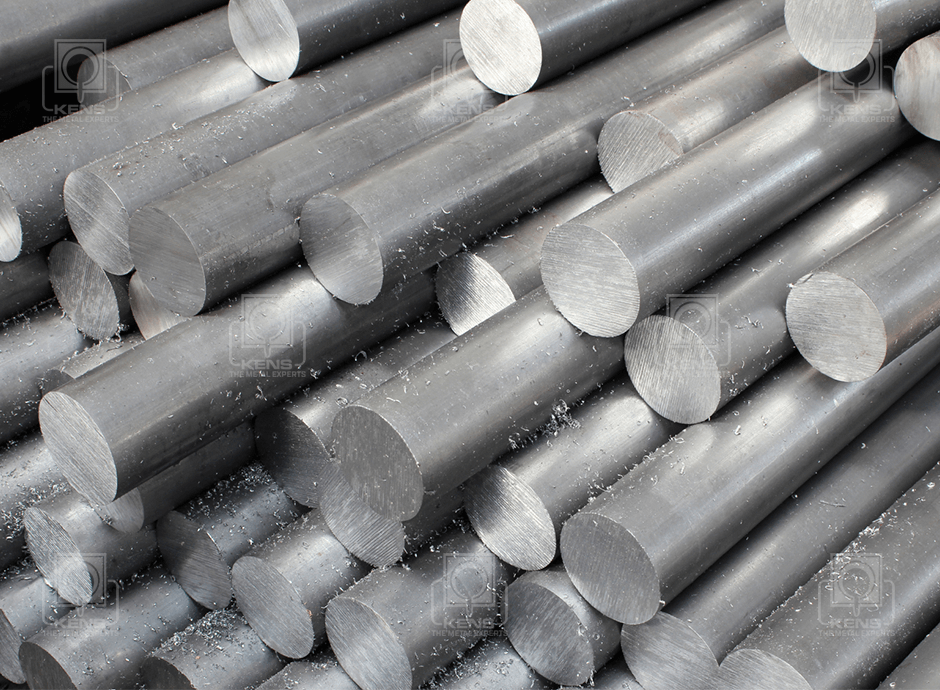
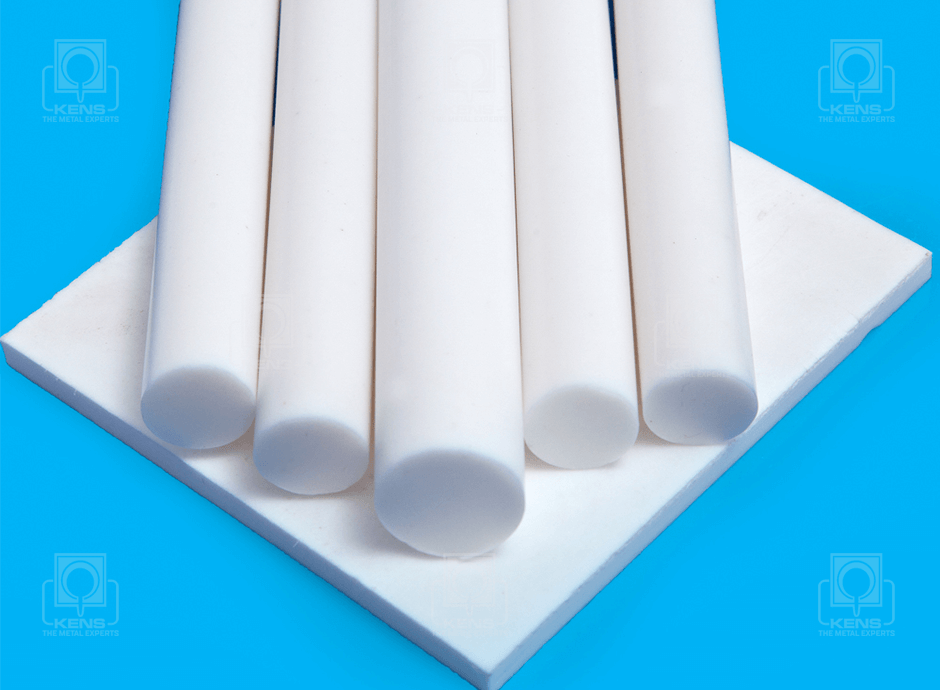
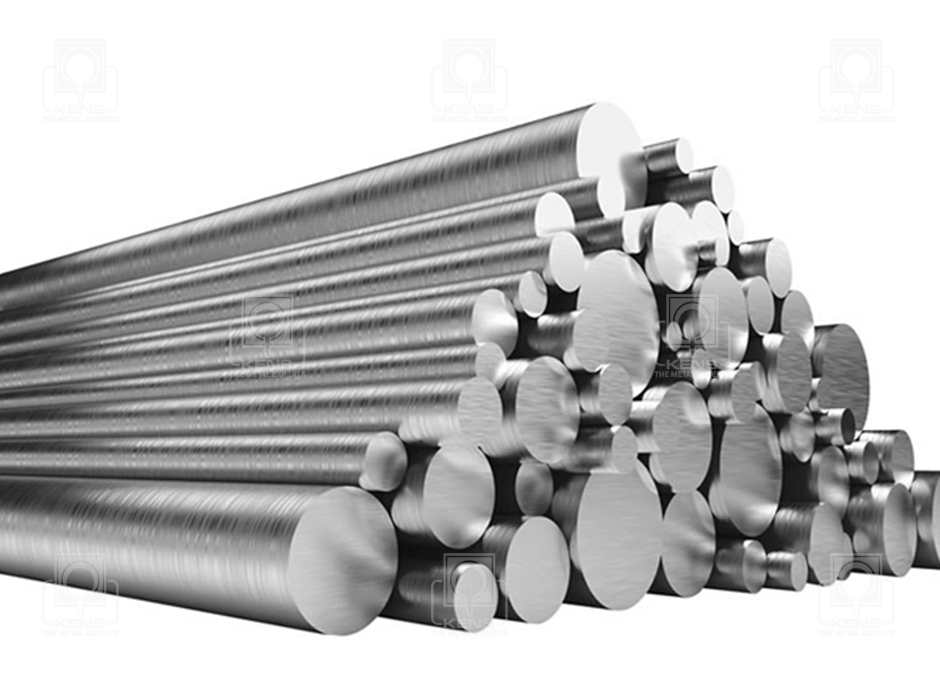







KENS METAL INDUSTRIES is a leading supplier and manufacturer of Engineering Materials in the East African region. The company operates under ISO 9001:2008 standards offering a wide range of FERROUS and NON FERROUS METALS to meet demands of various sectors such as Mining, Construction, Cement, Sugar, Pharmaceutical , General Engineering and other industries.
View Brochure Download Engineering Brochure Download Brass/Aluminium Ironmongery Brochure